Developer Guide¶
This GUI is constructed on the top of Qt framework (Qt for Python).
Dependencies¶
Architecture¶
The classes in module are listed below.
m2gui¶
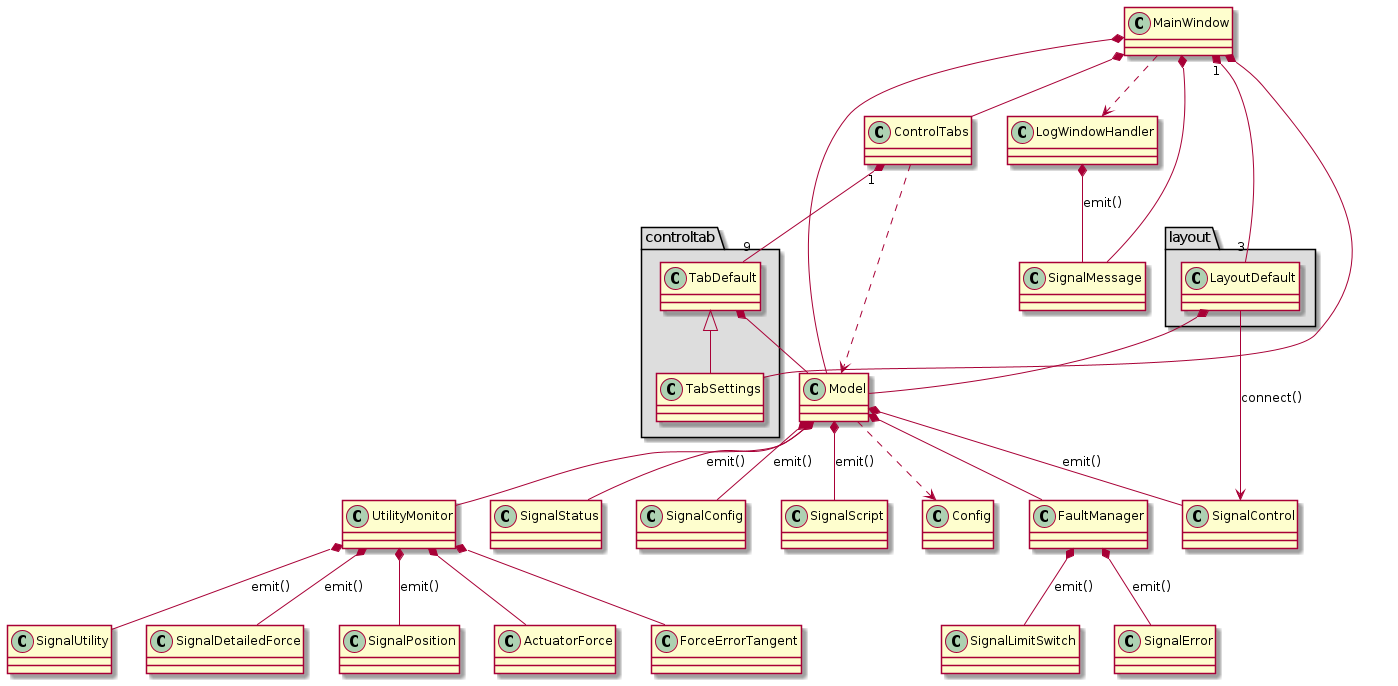
Figure 14 Class diagram of M2 GUI¶
MainWindow is the main window of the application.
Model contains the main business logic in the application.
Config is a data class that has the configuration details in the M2 cell control system.
FaultManager records the system error.
UtilityMonitor monitors the utility status.
ActuatorForce is a data class that has the force details contain the look-up table (LUT) information, force balance system, etc.
ForceErrorTangent is a data class that is used to monitor the supporting force of mirror according to the tangential link force error.
ControlTabs has the control tables.
LogWindowHandler handles the log window.
The model–view–controller (MVC) architecture is used in this module. In this design, the view always shows the data sent from the model. This helps to minimize the business logic in view and makes the tests easier. If you want to cache the data for a smooth showing in view, you need to do this in the Model.
The Qt signal is used to do the data exchange.
The emit() and connect() in the class diagrams mean the class emits a specific signal and connects it to a specific callback function.
The controller is reused from the ts_m2com.
Most of signals are holded and emitted from the Model or its components to simplify the management of signals.
Only the SignalMessage is holded by the MainView.
The SignalMessage is unrelated to the Model, which is only used to show the logged message on the overview table.
Qt provides its event loop that is different from the event loop in Python asyncio library.
The qasync allows coroutines (async/await keywords) to be used in PyQt/PySide applications by providing an implementation of the PEP-3156 event-loop.
For the other tasks in a loop to run, an awaitable must be called from another coroutine.
This allow for the coroutine to claim CPU and performs its operations.
Therefore await asyncio.sleep() calls are placed in unit tests calls, so the signal handling etc. can occur.
m2gui.signals¶
The available Qt signals are listed below:
SignalControl sends the event that the control is updated or not.
SignalError sends the error code.
SignalLimitSwitch sends the event of limit switch status.
SignalMessage sends the message event.
SignalStatus sends the event of system status.
SignalConfig sends the configuration.
SignalUtility sends the utility status.
SignalDetailedForce sends the calculated and measured force details contains LUT, force balance system, etc.
SignalPosition sends the rigid body position.
SignalScript sends the status of script progress.
m2gui.layout¶
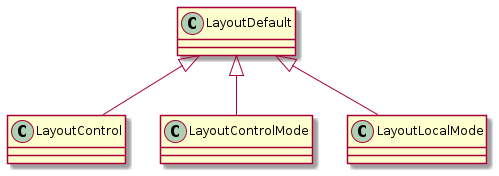
Figure 15 Class diagram of layout module¶
LayoutDefault is the default parent panel of other child classes in this module.
LayoutControl is the panel of control.
LayoutControlMode is the panel of control mode.
LayoutLocalMode is the panel of local mode.
m2gui.display¶
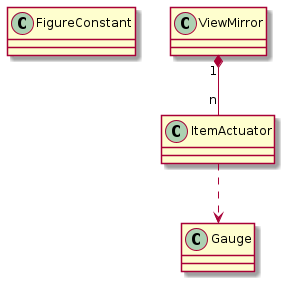
Figure 16 Class diagram of display module¶
ViewMirror is the view on the mirror populated by actuators.
ItemActuator is the actuator item used in the ViewMirror class to show the actuator information.
Gauge provides the color scale.
FigureConstant is the figure to show the constant line data in real-time.
m2gui.controltab¶
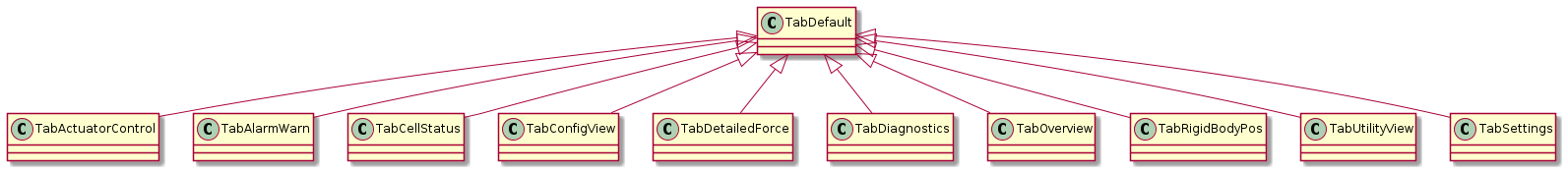
Figure 17 Class diagram of controltab module¶
TabDefault is the default parent table of other child classes in this module.
TabActuatorControl controls the actuator.
TabAlarmWarn shows the alarms and warnings.
TabCellStatus shows the cell status.
TabConfigView shows the configuration in the M2 cell control system.
TabDetailedForce shows the detailed force data.
TabDiagnostics shows the diagnostics information.
TabOverview shows the overview of system status.
TabRigidBodyPos controls the rigid body position.
TabUtilityView shows the utility status.
TabSettings shows the settings of GUI.
The class diagrams for each table child class are listed below to give you the idea of class relationship.
m2gui.controltab.TabActuatorControl¶
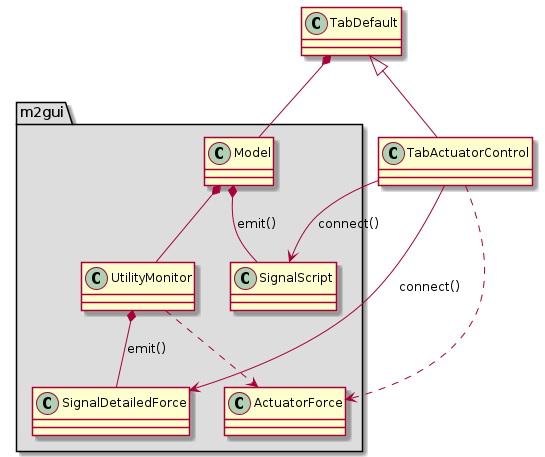
Figure 18 Class diagram of TabActuatorControl class¶
m2gui.controltab.TabAlarmWarn¶
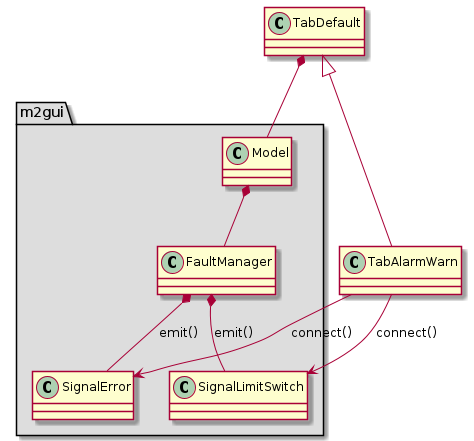
Figure 19 Class diagram of TabAlarmWarn class¶
m2gui.controltab.TabCellStatus¶
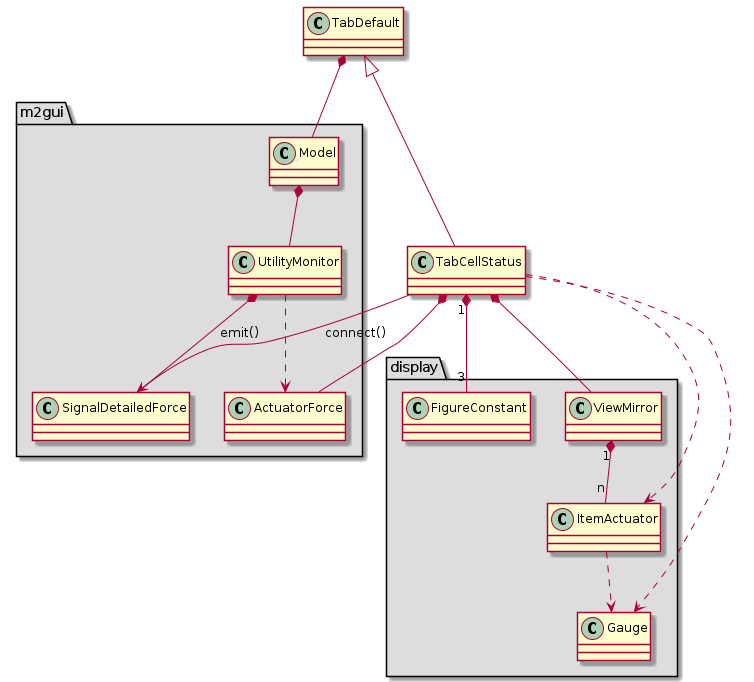
Figure 20 Class diagram of TabCellStatus class¶
m2gui.controltab.TabConfigView¶
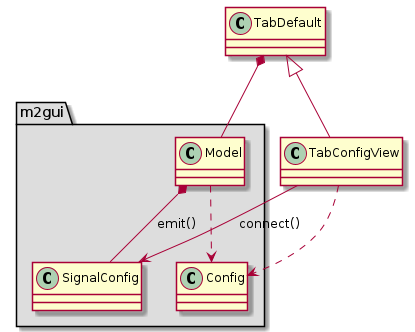
Figure 21 Class diagram of TabConfigView class¶
m2gui.controltab.TabDetailedForce¶
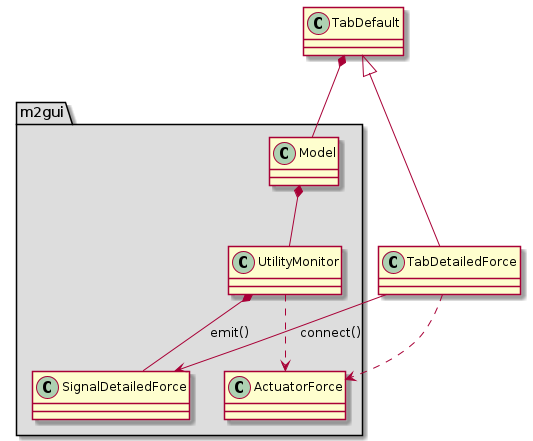
Figure 22 Class diagram of TabDetailedForce class¶
m2gui.controltab.TabDiagnostics¶
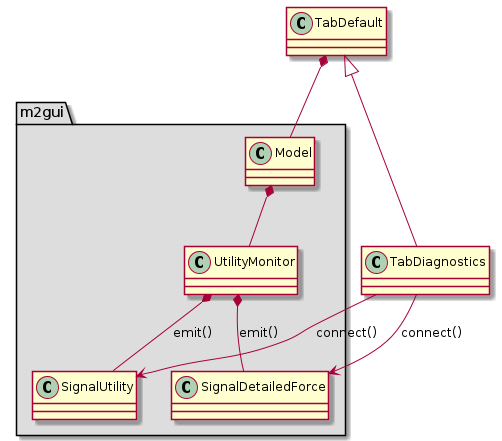
Figure 23 Class diagram of TabDiagnostics class¶
m2gui.controltab.TabOverview¶
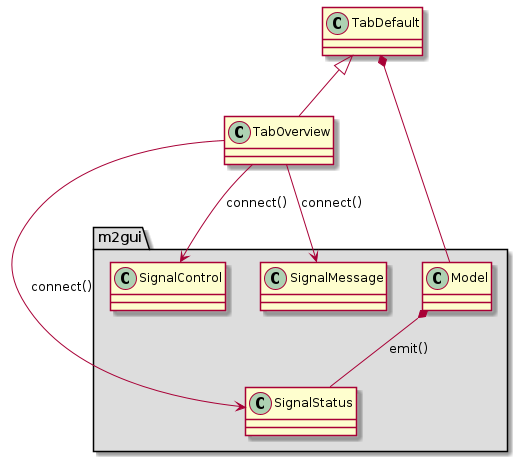
Figure 24 Class diagram of TabOverview class¶
m2gui.controltab.TabRigidBodyPos¶
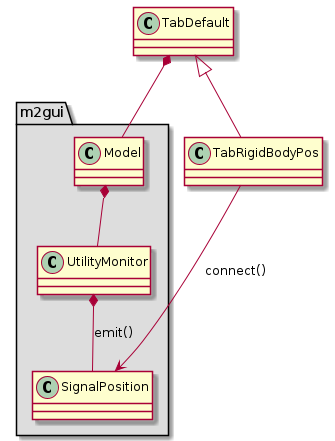
Figure 25 Class diagram of TabRigidBodyPos class¶
m2gui.controltab.TabUtilityView¶
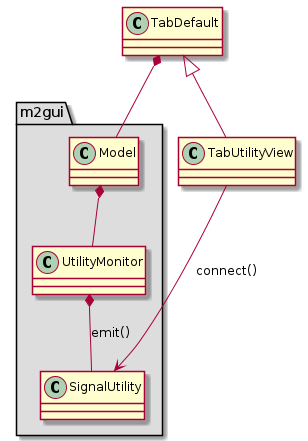
Figure 26 Class diagram of TabUtilityView class¶
m2gui.controltab.TabSettings¶
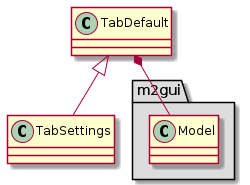
Figure 27 Class diagram of TabSettings class¶
APIs¶
This section is autogenerated from docstrings.
lsst.ts.m2gui Package¶
Functions¶
|
Create the group box. |
|
Create the label. |
|
Create the table. |
|
Get the number of actuators on the specific ring. |
|
Get the tolerance. |
|
Shows a warning dialog. |
|
Run the application. |
|
Run the command. |
|
Set the button. |
Classes¶
|
Actuator force class to have the force details contain the look-up table (LUT) information. |
|
Configuration class to have the configuration details. |
|
Control tables. |
|
Direction of the displacement sensors. |
|
Fault manager to record the system error. |
|
Select the actuator data to show on the figures. |
|
Tangential link force error class to monitor the supporting force of mirror. |
|
Type of the limit switches on actuators. |
|
Operation mode of the engineering user interface (EUI). |
|
Log window handler. |
|
Main window of the application. |
|
Model class of the application. |
|
Ring of the actuators. |
Configuration signal to send the configuration. |
|
Control signal to send the event that the control is updated or not. |
|
Detailed force signal to send the calculated and measured force details contains the look-up table (LUT). |
|
Error signal to send the error code. |
|
Status signal to send the event of limit switch status. |
|
Message signal to send the message event. |
|
Position signal to send the rigid body position. |
|
Script signal to send the status of script progress. |
|
Status signal to send the event of system status. |
|
Utility signal to send the utility status. |
|
|
Group of the temperature sensors. |
Utility monitor to monitor the utility status. |